Security Devices#
In daily security operations and key protection during special periods, the most important thing for security personnel is a variety of security protection devices, such as situational awareness, WAF, firewalls, EDR, honeypots, etc.
1. Firewall:#
Positioning: Access control products, the first type of security products after the emergence of networks.
Function: Isolate internal networks, external networks, and DMZ zones (the area where business systems are published externally, Web application servers, mail servers, etc.) and control user access.
Deployment method: Usually deployed at the network boundary or important system boundaries. Typically operates at the network layer.
2. IPS:#
Positioning: Access control products, Intrusion Prevention Systems. Function: Capable of analyzing and monitoring network traffic flowing through the device, and most importantly, after detecting an attack, it can promptly intercept and block it. It is an important complement to firewalls. If the firewall is the first line of defense, then the IPS is the second.
Deployment method: Usually connected in series on the main network link or at the boundary of important business systems, typically where firewalls are located, there is also IPS.
3. WAF#
Positioning: Access control products, Web Application Firewall. Function: Specifically targets traffic based on HTTP/HTTPS protocols, performing content detection and validation on various requests from Web application clients, ensuring their security and legality, and blocking illegal requests in real-time, thus effectively protecting various websites.
Deployment method: Usually deployed at the boundary of Web applications. Typically operates at the application layer.
Difference from firewalls: WAF and firewalls are two different types of products. Traditional firewalls operate at the network layer, providing access control and blocking based on IP addresses and ports, without protecting or filtering at the application layer. WAF focuses on the application layer, parsing and filtering all WEB application information, addressing web security issues such as injection attacks, web tampering, web shell attacks, and sensitive information leakage.
Difference from IPS: Although both can resist attacks and have overlapping functions in detecting and intercepting many attack behaviors, the biggest difference between WAF and IPS is the protection of WEB applications. IPS has a wide range of protection; it detects and intercepts any discovered attack behavior, including the analysis of HTTP/HTTPS traffic. WAF is solely responsible for protecting WEB systems, with more complete and comprehensive bidirectional decoding and analysis of HTTP/HTTPS traffic, capable of addressing various security threats in WEB applications, such as SQL injection, XSS, cross-site request forgery attacks, cookie tampering, and application layer DDoS attacks. In terms of professional WEB protection, WAF is much stronger than IPS.
Security Incident Analysis Ideas and Logic#
In general security operations and during critical protection, the most commonly used device by security engineers is the IPS mentioned above. Competent security vendors also develop their own IPS devices. Below, we take a specific device as an example to explain the entire security monitoring thought process.
Prioritize Security Events on Real-Time Attack Analysis Pages#
The alarm pages of IPS devices are generally quite similar. Taking the following image as an example, we can filter the alarm information to be displayed by selecting different variables, including the range of assets of concern, the types of events to prioritize, the severity level of events, attack status, etc. We can also link with other security devices to block suspicious IPs and whitelist IPs that have been cleared of risks.
Discover Attack IPs by Viewing Security Alarm Details and Block IPs#
When multiple attacker IPs belong to the same network, once confirmed as malicious, the entire subnet can be blocked.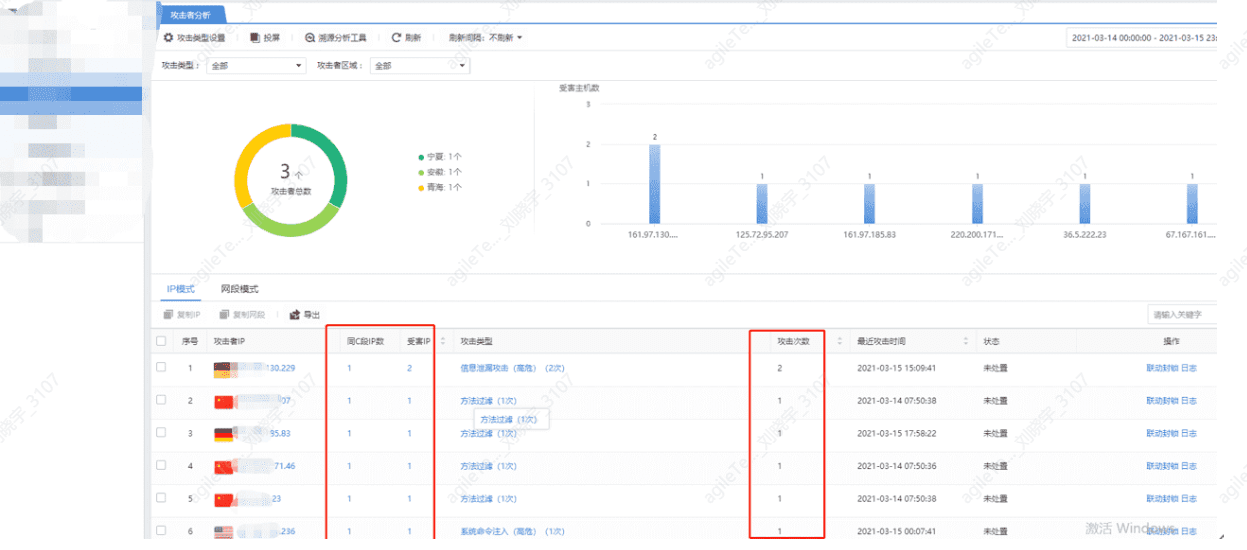
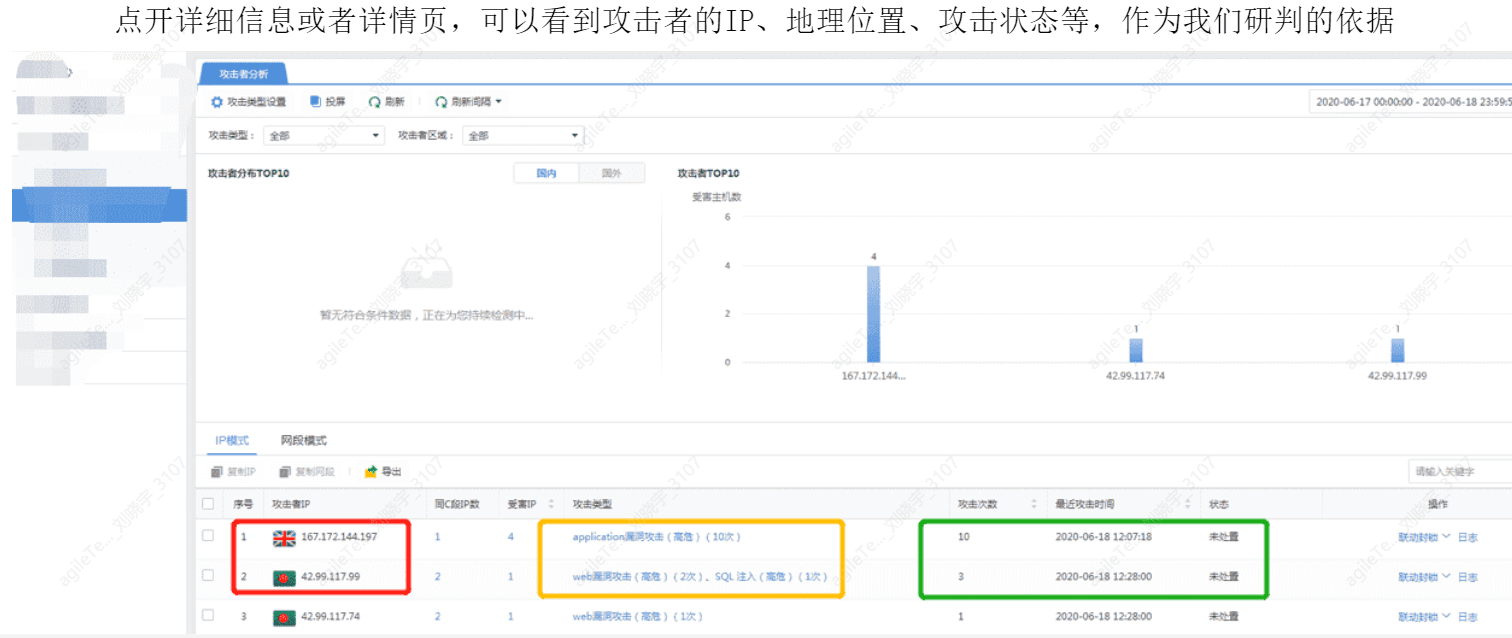
The Alarm Information Displayed on the Security Device Alarm Page is Generally Aggregated Threat Intelligence#
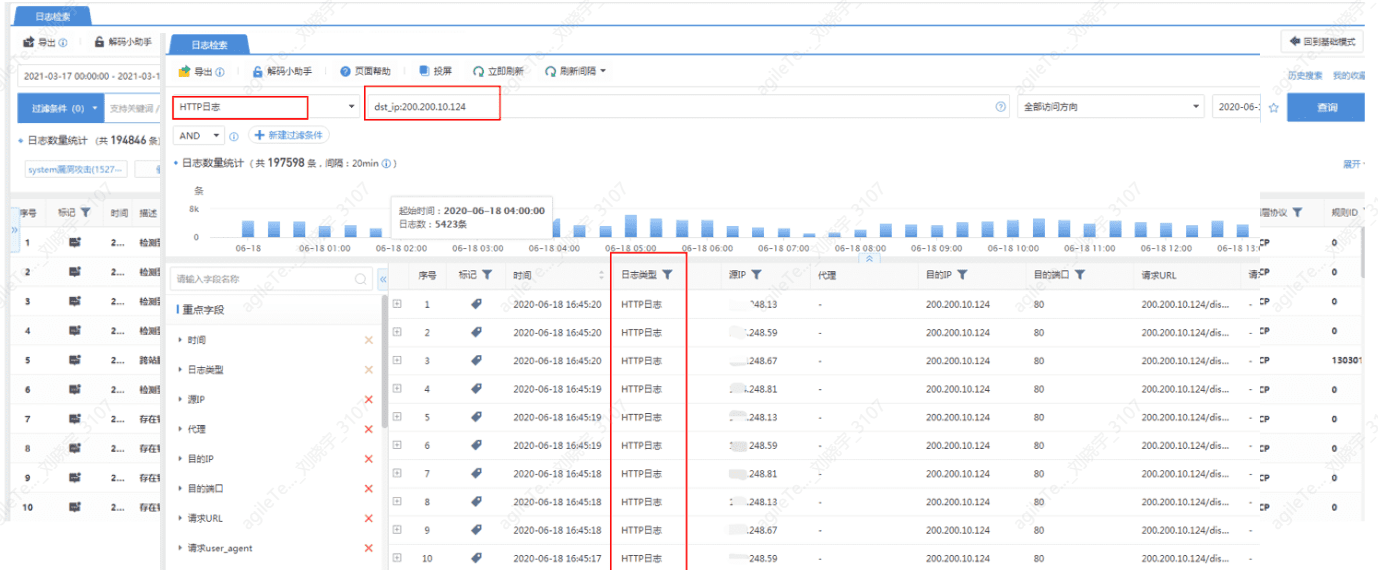
If targeted analysis of security detection information or HTTP audit logs is needed, it can be searched in the log center.
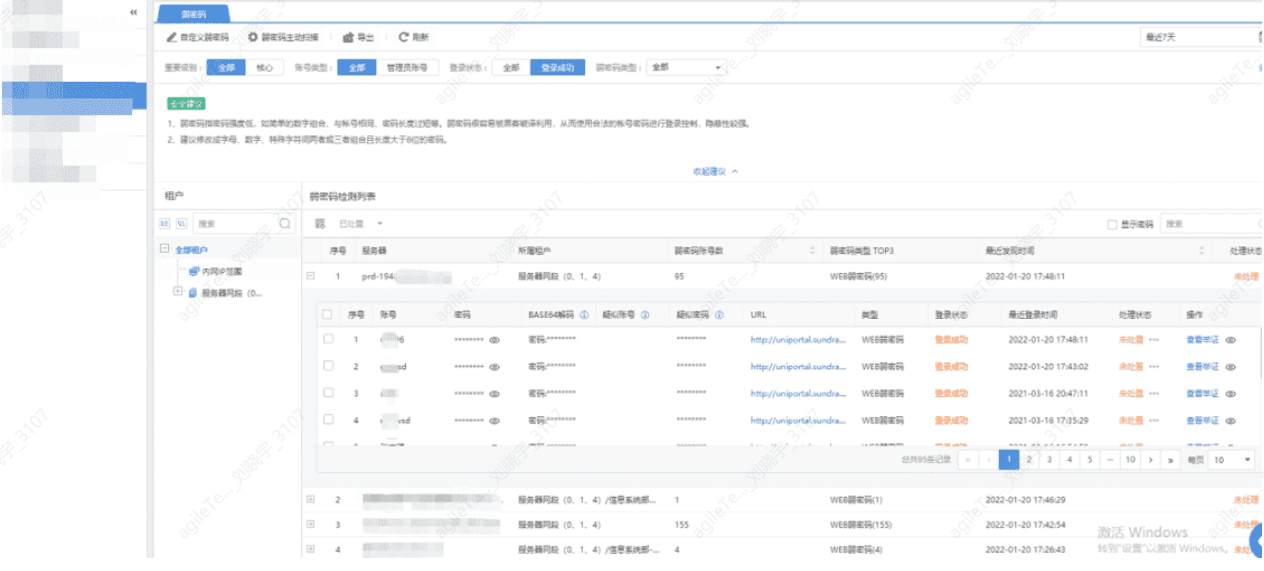
Other Additional Engineering of Security Devices#
Such as recent vulnerability checks, weak password checks, system vulnerability checks, etc., these can be carried out as needed at any time.
Common Attack Alarm Analysis#
Brute Force Attacks#
Account cracking, as a low-cost attack method, is very favored and ranks among the top few attack methods. Its basic characteristic is a large number of login requests in a short period. The points of attack are numerous, including SMB, email, FTP, SSLVPN, RDP, SSH, Telnet, MySQL protocols, etc.
False positive exclusion methods:
- Check logs: Brute force attack security events come from audit logs or brute force attack security logs.
Check the time to see if there are continuous large amounts of access logs or brute force attack security logs, and confirm whether the intervals between each brute force attack security log are similar.
- Check event trends to see if there have been a large number of accesses over a period of time, as shown in the figure:
A large number of requests initiated in a short time are generally not false positives and need to be investigated on the corresponding terminal.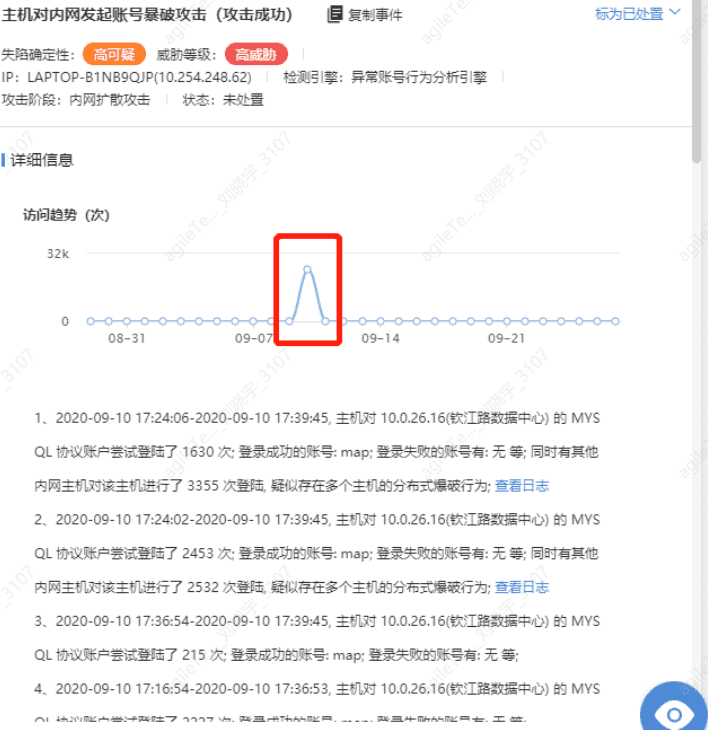
- Check the login logs on the terminal to see if there are a large number of login failure logs. The methods for checking brute force attacks vary by protocol.
Windows system log location: RDP/SMB can find the login event 4625 in the event viewer.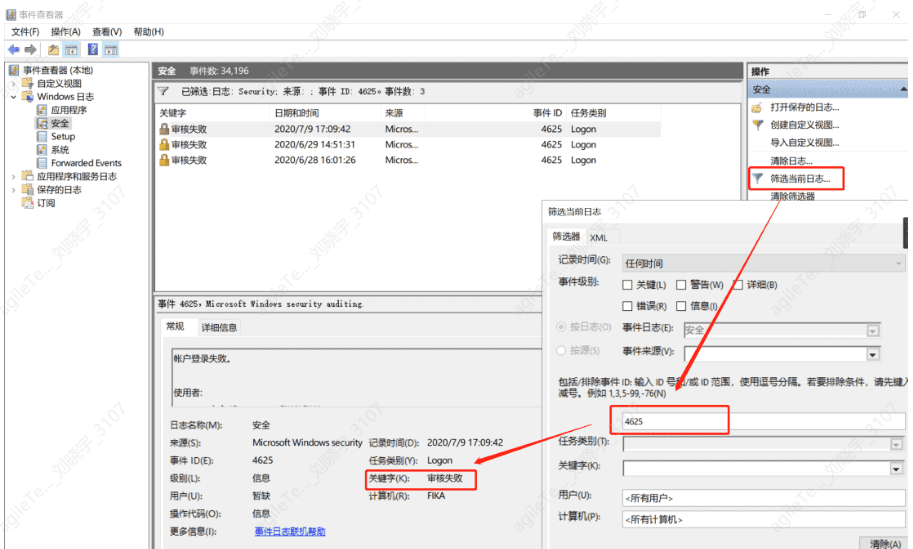
Linux:
Query UID 0 users
awk -F: '$3==0 {print $1}' /etc/passwd
Check users with sudo privileges
more /etc/sudoers | grep -v "^#|^$" | grep "ALL=(ALL)"
Information on accounts that can log in remotely
awk '/$1|$6/{print $1}' /etc/shadow
This command can query failed login records, but I may have entered it incorrectly and found nothing, possibly because the virtual machine has not had any failed logins.
Web Path Detection#
Suspicious IPs or internal main sentences have requested a large number of web directories of the target system in a short time.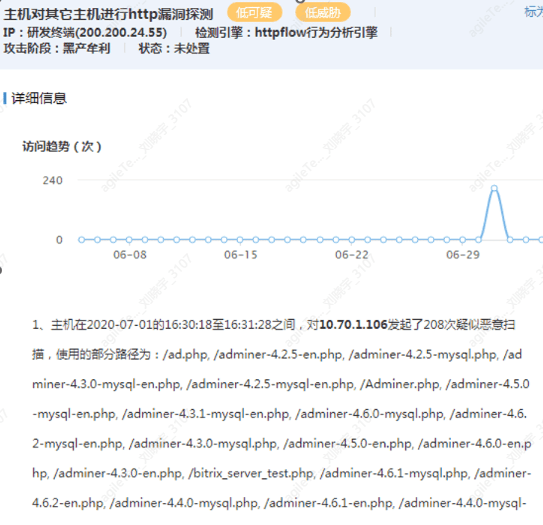
False positive exclusion methods:
1. If a large number of non-existent web pages are scanned in a short time (speed unattainable by humans, such as reaching 208 times in just over a minute), it is very likely probing whether some middleware exists.
2. Check if the scanned paths include common middleware URLs, such as continuously scanning whether MySQL management tools exist. If scanning reaches MySQL management tools, it may exploit vulnerabilities in tools for penetration, which is not a false positive. Alternatively, scanning for web shell paths may involve scanning for strange non-existent pages, such as xx.php/db.php/shell.php, etc. Scanning paths generally follow certain patterns, which can be categorized as follows:
a. Database management pages (phpmyadmin, adminer, etc.)
b. Backend management pages (manage.php, admin.php, etc.)
c. Specific paths for text editors (ewebeditor, ueditor)
d. Some web shell addresses (shell.php)
3. If the paths contain ordinary HTML pages or the client's own business pages, it is a false positive, such as scanning many index.index.html default.php, etc. This scenario generally involves a large number of requests generated by the client's normal business.
EternalBlue Vulnerability Exploitation Attacks#
EternalBlue and similar vulnerability exploitation attacks are identified through IPS rules and belong to system vulnerability attacks. The data packets cannot be viewed directly.
False positive exclusion methods:
Eternal system vulnerability false positives are rare. If one host initiates attacks on multiple hosts, it is generally not a false positive. You can also check if the host has other behaviors, such as scanning. Check the logs for any logs of exploitation attacks accessing port 445; the data packets are in hexadecimal.
1. You can view the content by converting hexadecimal to characters https://www.bejson.com/convert/ox2str/, to see if the content is a false positive. Other system attacks with hexadecimal data packet records can also try using this method.
WebShell Upload#
Detecting web shell uploads involves submitted requests containing files with web shell characteristics or one-liner trojan fields. Web shells can be searched online.
1. If the logs show garbled characters (actually binary and unreadable), it can be judged as a false positive.
2. If the link indicated by SIP downloads a normal file, it can also be judged as a false positive.
If you are unsure, you can upload the sample's MD5 or the sample to VirusTotal or Weibu Cloud Sandbox for inspection.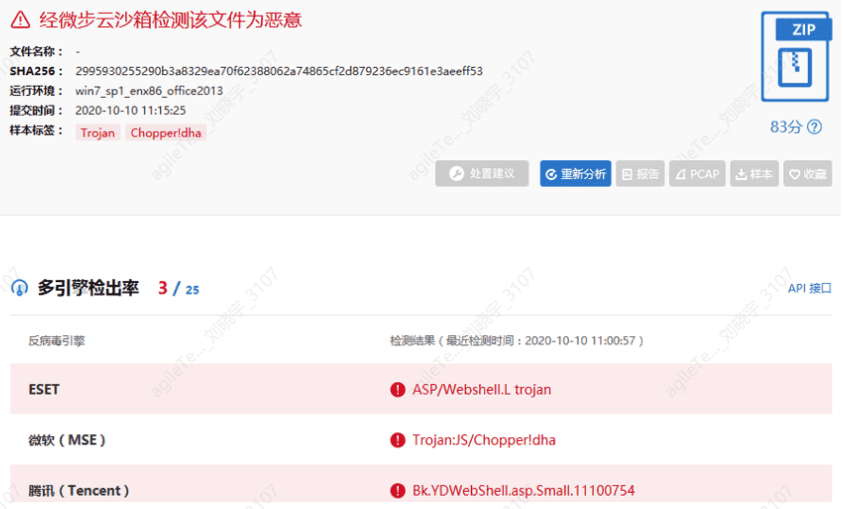
3. If multiple logs show that the submitted data packets are the same web shell file, it can be determined whether it is the client's business behavior, indicating a false positive. As shown in the figure, all logs are the same, indicating client business behavior.
4. If the code format is complex, containing dangerous functions like eval and various encoding conversions and encrypted strings, it is generally a true positive.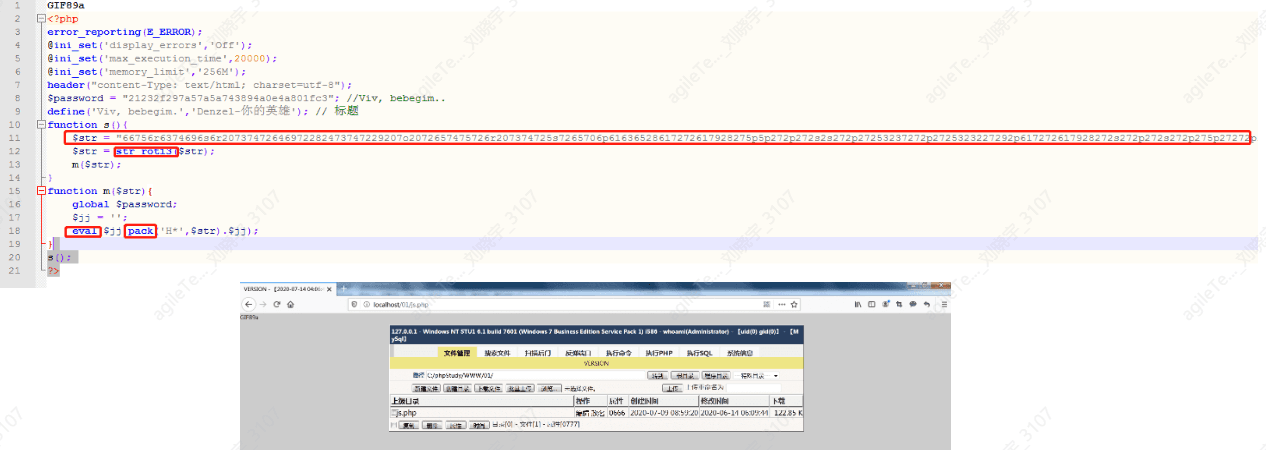
5. For encoded web shells, decoding is required. The Accept-Charset field value should be base64 decoded.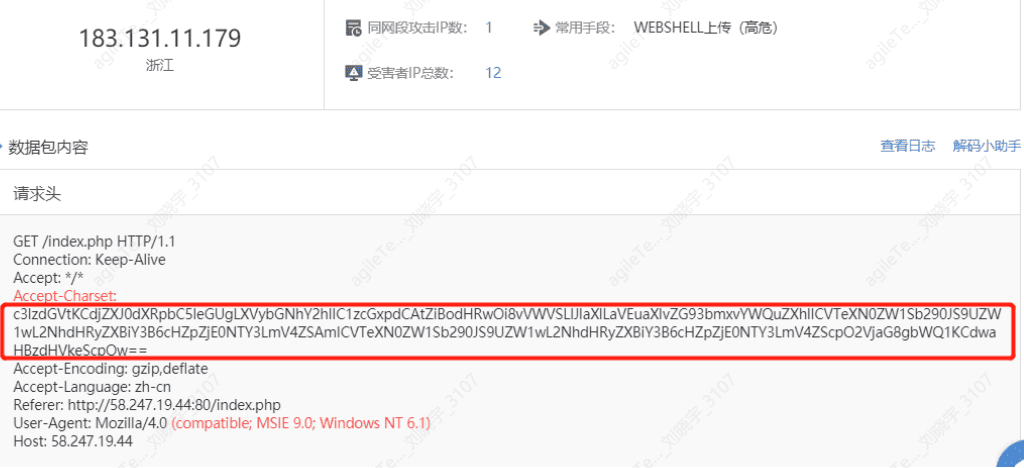
The decoding result shows the following image, containing sensitive keywords such as syetem(), echo(), certutil.exe, and not involving business content, indicating real vulnerability detection behavior.
SQL Injection Attacks#
SQL injection is judged by checking whether there are database query statements or keywords in the fields submitted in web requests.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. Check logs to see if there are keywords for database queries, such as select, where, union, etc., and determine whether the submitted statements are caused by the client's business requests being non-standard.
(PPT missed slides 2-5, possibly deleted)
6. Determine whether the attack was successful by checking the returned packets. The following figure indicates an attack behavior, but there are no returned packets, indicating the attack was unsuccessful.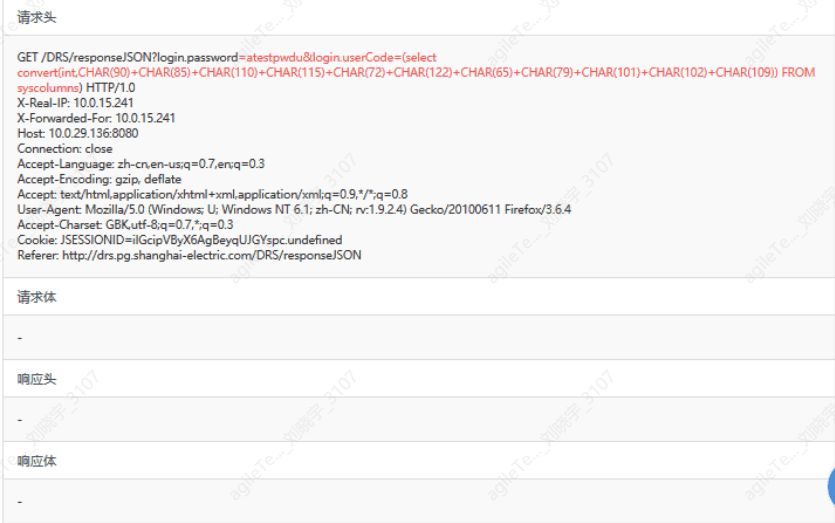
XSS Attacks#
Check whether there are or similar transformed strings in the logs; these belong to probing attacks.
Check whether there are external URLs in the logs; these addresses may be used to receive administrator information from third-party platforms.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. If a large number of XSS attack logs appear, but the log content format is the same with no obvious changes, it may be a false positive.
2. If the attack logs are in JSON format, confirm with the client whether it is normal business; if it is normal business, it is a false positive.
Scanning Attacks#
Divided into IP scanning and port scanning, where a large number of IPs or ports can be accessed within a certain time. When scanning IPs, the IPs will be recorded, but when scanning ports, the ports will not be recorded.
1. When a risk host accesses multiple hosts' port 445, it will be considered a scanning behavior. Other protocol scanning behaviors are similar. It is necessary to audit the normal access traffic, and the connection duration will be very short, with each scanning interval also being very short.
2. Hosts are subjected to TCP port scanning from external hosts.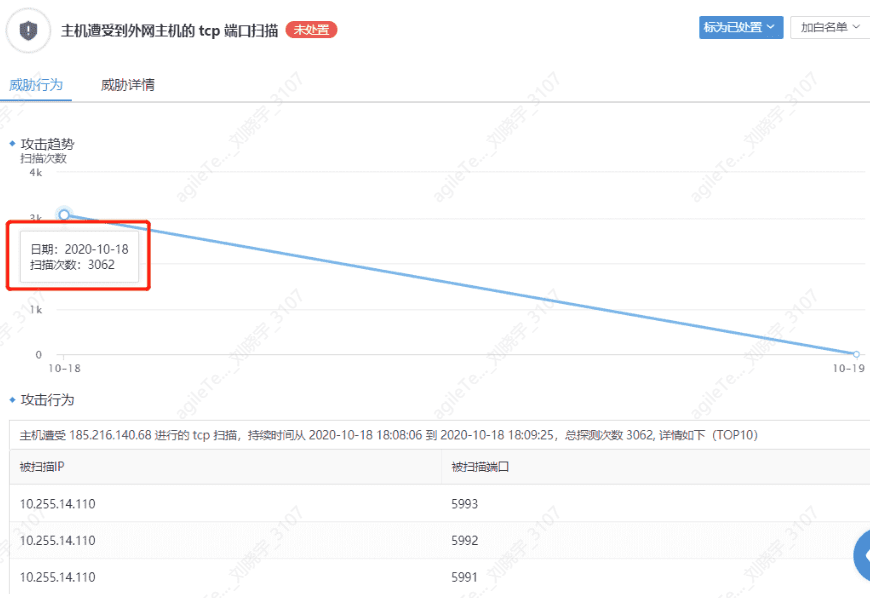
False positive exclusion methods:
1. You can directly determine through the platform netflow (network traffic logs). IPS needs to record the corresponding directional network traffic logs in advance. For host-initiated scanning events, directly set the filtering condition in the logs to: src_ip. Filter out all network traffic logs of that IP, click the small funnel for the destination port, and check if there are a large number of port records. If there are a large number of port access records, and each port access count is small, it is considered a true positive for port scanning.
For IP scanning, check whether the destination IPs are multiple and whether they belong to the same subnet; the thought process is similar.
2. If scanning behavior is still detected, you can check the connection status on the terminal using process analysis tools like Huorong Sword or SIP closed-loop tools, which can monitor network connections for a period, discover connected processes, and confirm whether it is a false positive. Other scanning protocol judgment methods are similar.
3. After confirming it is a scanning event, ask the client whether any similar operational tools are running; if so, whitelist the tool's IP.
4. If the detected scanning event has a constant destination port and scattered destination IPs, it is likely the behavior of P2P applications. You can confirm by searching online for the scanned ports.
5. For hosts subjected to scanning behavior from Internet hosts, confirm whether the host has open ports.
(1) Whether it is needed for business; if not, it is recommended to close the mapping relationship through exit devices.
(2) Confirm whether it is client business behavior.
Scanning Attack - System Command Injection#
For system command injection, after detecting relevant alarms, you can directly check the log retrieval center to see the submitted system commands.
Such as "rm -f", "cmd", "cd", etc.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. You can verify with the client whether there is such behavior in the business; if not, it can be judged as an attack.
2. If the returned packet is garbled and it is confirmed that the transmitted data is not encrypted, it can be determined whether the request data type is an image or something else that causes it to display as garbled. It can be judged as a false positive.
Struts2 Attacks#
Struts2 is a security issue caused by remote command execution. This vulnerability is triggered by modifying the Content-Type value or other fields in the HTTP request header, leading to remote code execution.
The following image shows that the request data packet's body contains malicious code such as echo, cmd, bin/bash, which is identified by the platform as remote code execution.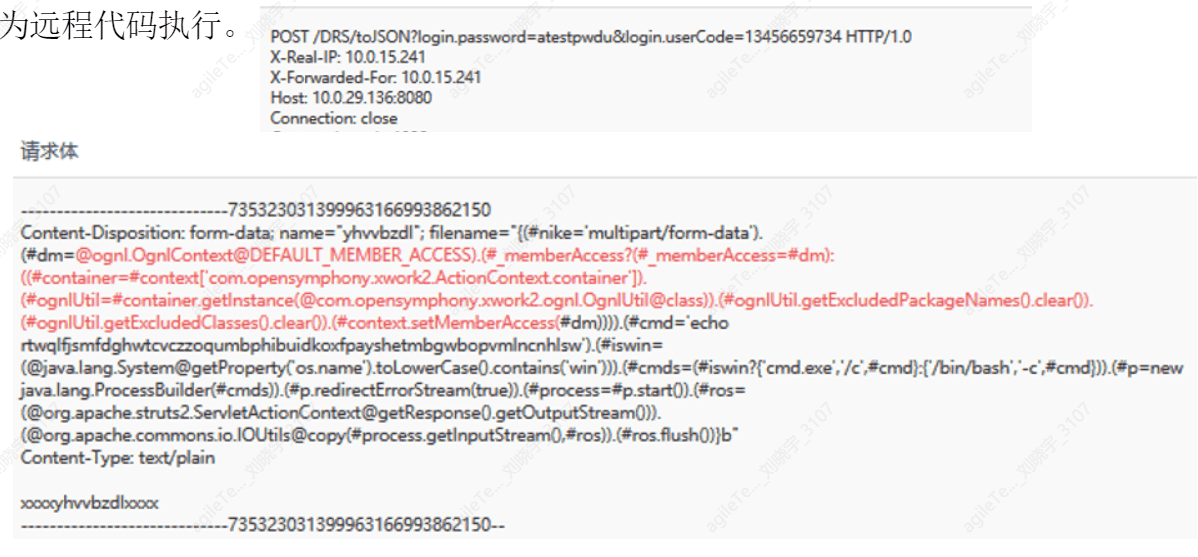
False positive exclusion methods:
1. First, check the Content-Type field; normally, the submitted Content-Type should be a file type field and not an execution statement.
2. Not all attack payloads for Struts2 attacks are in the content-type. The core investigation idea should be to check whether the request direction data contains deserialization code, such as java.getruntime. If it exists, it is generally not a false positive. As for whether the attack was successful, it depends on whether the commands in Java have corresponding results output on the response page. In the attack example above, cmd='netstat -ano' is querying the port connection status, so check the response page for corresponding return data.
The following image shows no return data, indicating the attack failed.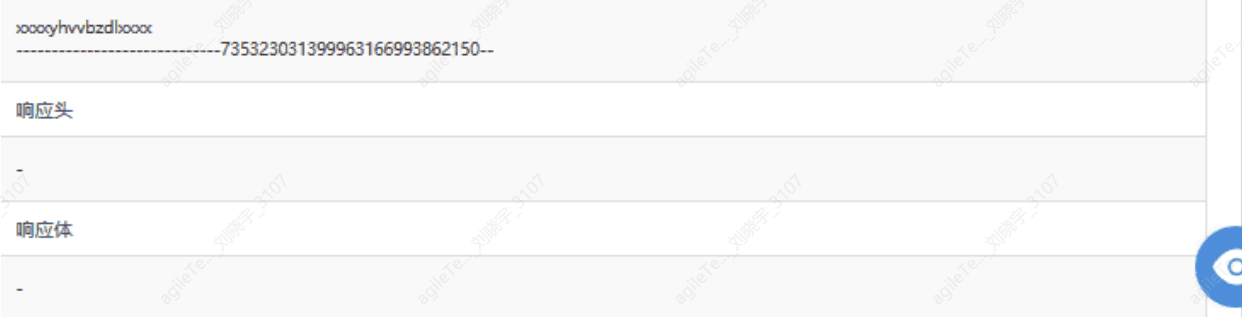
Directory Traversal Attacks#
The judgment criteria are simple; as long as the request contains ../ or .., it will be judged as a directory traversal attack.
False positive exclusion methods:
Confirm the business situation of the host to see if there are characters like "../" in the business transmission data packets that are easily recognized as directory traversal. As shown in the figure below, the data packet contains malicious code such as ../../../ ../../ ../ etc/passwd.jpg, attempting to traverse the contents of etc/passwd, indicating real attack behavior.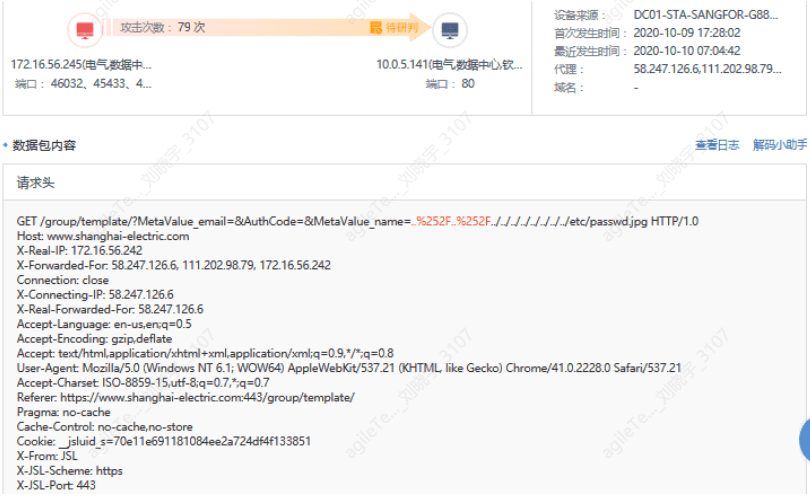
Determine whether the attack was successful.
The following image shows that no relevant sensitive information was returned in the response, indicating that the attack was unsuccessful.
Email Security#
Email security includes security issues in virus emails, spam, and phishing emails in sent and received emails. It can only detect security events in pop3/imap/smtp and web HTTP emails and does not support detecting encrypted emails.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. Virus emails
Determine whether the attachment information downloaded from the email is a virus; you can upload the file's MD5 to VT for confirmation.
2. Spam emails
Determine whether the email content or subject contains keywords for spam information.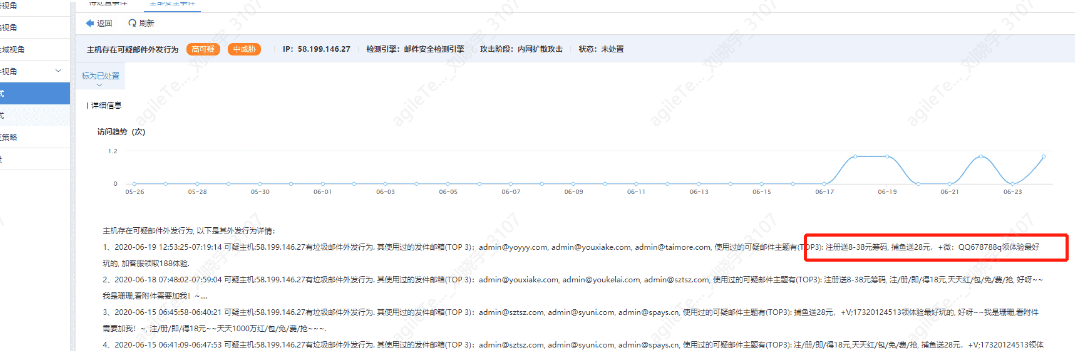
-
Phishing emails
Determine whether the URLs or files in the email are malicious.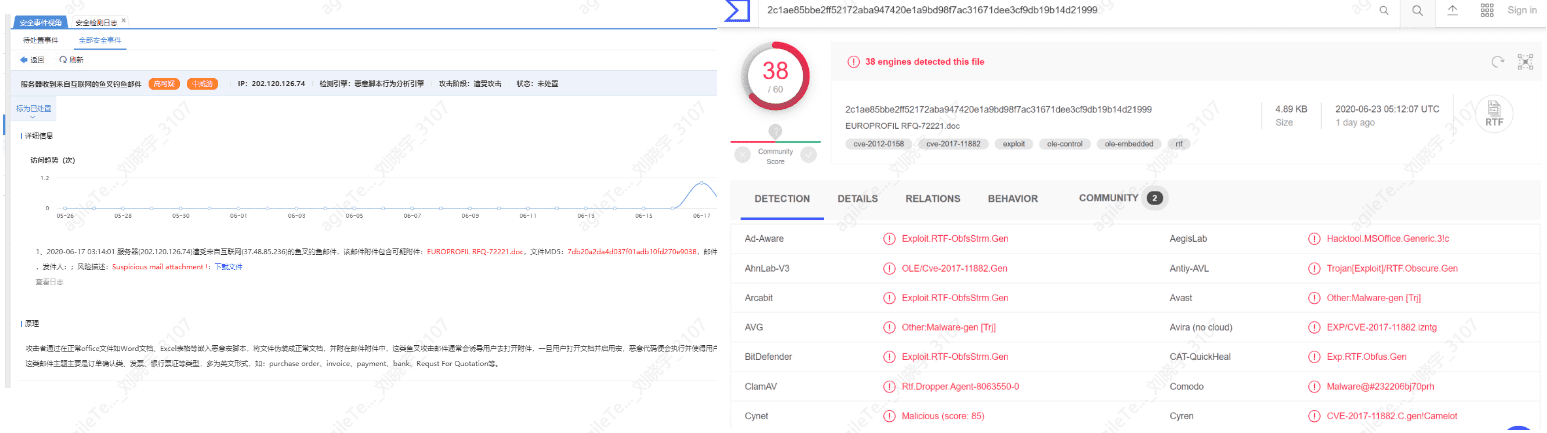
-
The host exhibits suspicious email sending behavior
Detection principle: Determine whether the host has used too many domain emails for sending emails.
If the email business of the host is the client's normal business, it is a false positive; otherwise, the host may be infected with a mailer, and abnormal processes need to be checked.
Information Leakage Attacks#
Information leakage attacks occur when the server returns version information of the system, middleware, etc., after an attack request is initiated. Hackers can find corresponding vulnerabilities through the returned version information and launch attacks.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. Check whether the log data packets contain feedback version information, phpinfo information, or website source code.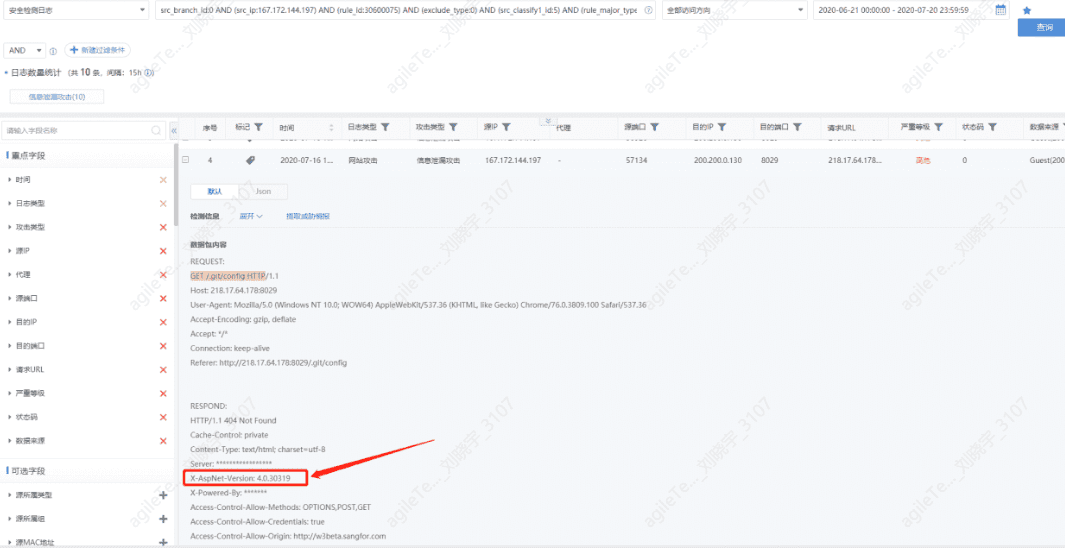
2. If the feedback content does not contain version information, you can expand and check the accessed paths. If no useful information is found, it can be confirmed as a false positive.
Threat Intelligence Detection#
For example, accessing a certain family’s communication domain.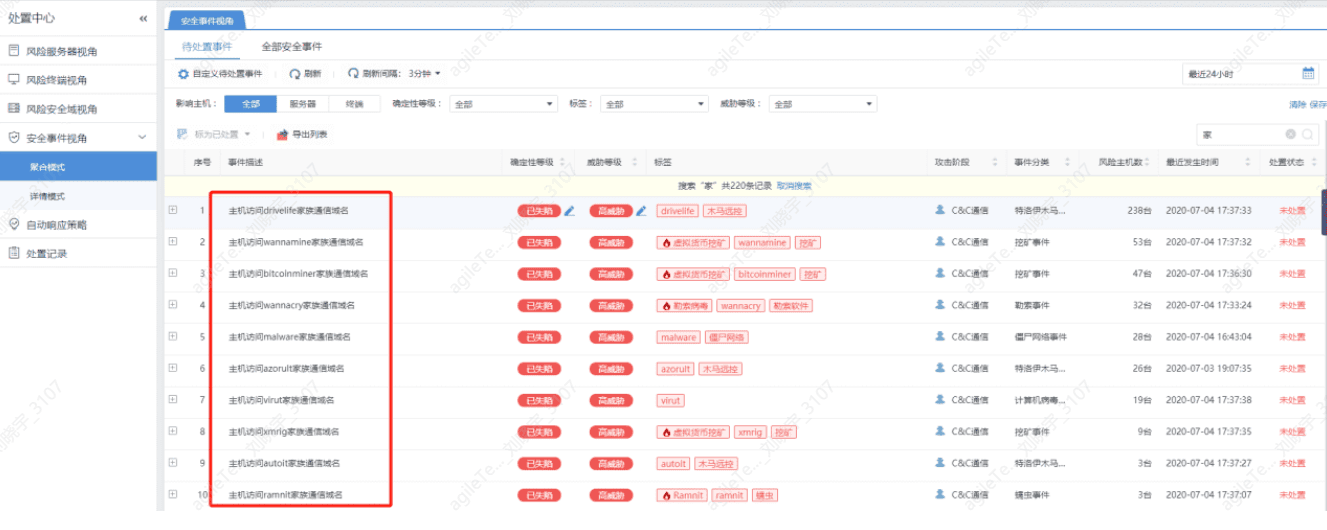
False positive exclusion methods:
The following analysis process uses all security events accessing malicious domains. Analysis steps:
1. Check the detection results on wiki.sec.sangfor.com.cn.
Or go to Weibu or VT for further confirmation. If there is nothing on Weibu or VT, follow the steps below.
3. Use EDR and other endpoint security devices for a full scan, ensuring that the device's rule library is updated to the latest version during the scan.
4. If EDR does not detect any threats, confirm whether the client's host has antivirus software installed, check the antivirus records, and whitelist records for any suspicious virus files.
Webshell Backdoor#
Webshell backdoor events are those detected after a web shell has been uploaded to the web server and accessed. These are post-event security incidents.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. Detected web shell backdoor false positives are rare, with some cases of missed detection. Access to web shell traffic is required for identification. You can directly find the backdoor file as shown in the figure below, and then use D Shield on Windows to check it for confirmation.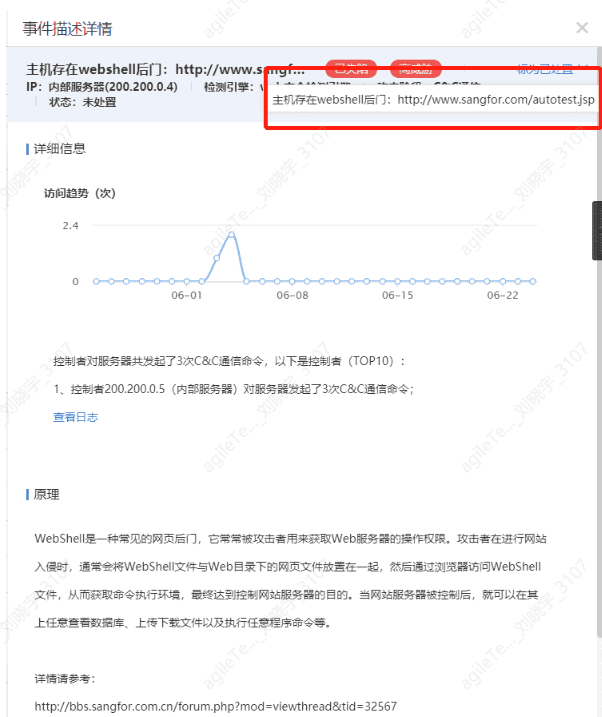
Black Links#
Identifying websites with black links through keyword detection, such as gambling-related keywords.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. The client's website posts may contain black link keywords, leading to false positives.
2. Some slightly advanced black links may not be visually detectable on the interface; you can use a browser to view the source code to find black link keywords.
3. More advanced black links may not be directly visible in the source code and may call JS functions, making them visible to search engines but not when opening the website. You can use Burp Suite or Wireshark to access the website and track the calls to discover the black link invocation addresses.
Shell Rebound#
Can only be viewed in the log detection center; it detects whether the host has external SSH connections, which will be judged as shell rebound.
False positive exclusion methods:
Most are false positives; there are only logs, no security events.
If there are still connections, you can use process analysis tools on the host to monitor the connection status of the processes connecting to the destination port reported by SIP.
HTTP Timed Requests for Suspicious Files#
By periodically downloading malicious files, the virus is kept alive. Requests are made to the external network at certain time intervals.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. Check whether the download time has timed characteristics, such as the above screenshot showing that the host downloads malicious programs once an hour. If there are no timed characteristics, there may be an issue with the algorithm.
2. Query the threat intelligence information of the domain/IP in the download URL. If the domain or IP is blacklisted, it is generally not a false positive.
3. Directly place the URL into an open-source cloud sandbox (such as VT, Weibu Cloud Sandbox); if the URL is still valid and can be detected as malicious, it is definitely not a false positive.
4. If there is no information on threat intelligence and the URL has expired, you can Google the reputation of the domain/IP; if it belongs to a normal company, it may be a false positive.
Downloading Forged Files#
By comparing the file extensions with the file header information detected by SIP, if they do not match, it is a forged file.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. Check whether the file extension in the URL matches the file header; for example, if the file extension in the URL is a rar compressed file but the file header is actually an ELF executable file, this would not be a false positive.
2. Generally, many domains/IPs in the URL have also been included in threat intelligence, allowing for relevant threat intelligence to be checked.
3. If it is the client's own business and there is indeed an executable file with an incorrect extension, it can be defined as a false positive (this situation is very rare).
The Host Exhibits Behavior of Downloading Malicious Programs#
By downloading executable programs via HTTP, the threat intelligence of the domain/IP/url is used to identify whether the download is malicious.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. The most commonly used method is to check the threat intelligence of the domain/IP in the URL; if it is blacklisted, it is accurate; if it is a well-known website, it is a false positive.
2. You can still use the URL to check in the cloud sandbox (VT) for malicious detection.
The Host Exhibits Risks of Malicious Data Leakage#
Situations of successful directory traversal, .svn/.git source code leakage, backup source code leakage, and backup database file leakage occur.
False positive exclusion methods:
Sensitive information leakage mainly falls into several situations: successful directory traversal, .svn/.git source code leakage, backup source code leakage, and backup database file leakage, which can be directly accessed by visiting the URL, making it quite obvious. For example, in the situation below, the .svn directory is placed in the web directory and accessed, which can lead to source code leakage.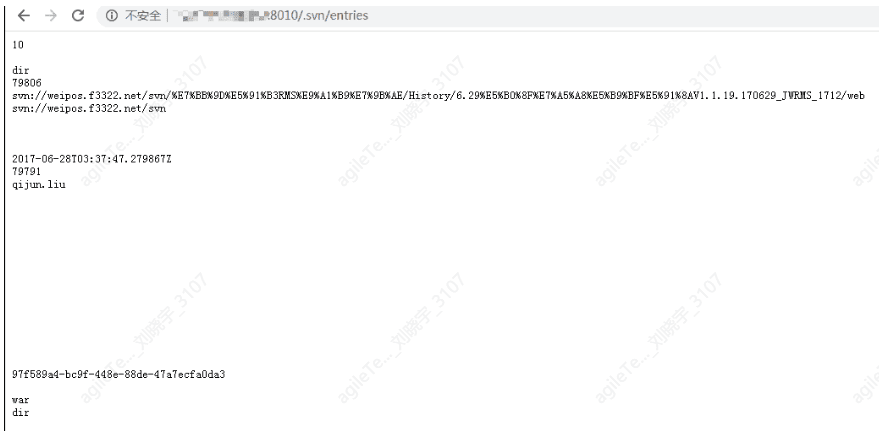
The Host Exhibits Cobalt Strike Communication Behavior#
The domains/IPs contained in the URL are mostly C2 servers.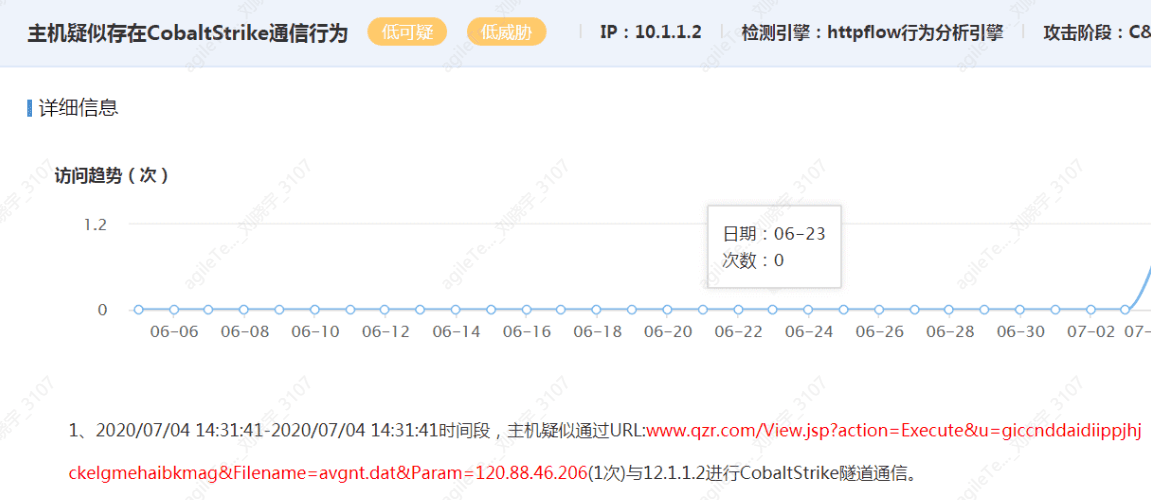
False positive exclusion methods:
1. First, confirm whether the detected IP and suspicious paths point to the unit's normal business.
2. If the detected paths are abnormal business rather than Internet resources, you can query the relevant URL/IP information on VT and Weibu, and download samples from the URL for antivirus detection/manual inspection.
The Host Exhibits ICMP Tunnel Communication Behavior#
Tunneling technology is a way to transmit data between networks using the infrastructure of the Internet. The data transmitted using tunnels can be data frames or packets of different protocols. Tunnel protocols repackage data frames or packets of other protocols and send them through the tunnel. ICMP tunneling encapsulates data in ICMP protocol ping packets, taking advantage of the fact that firewalls do not block ping packets to transmit data.
For example, the host is suspected of communicating with multiple hosts via ICMP tunneling, totaling 517 times, which is quite frequent and needs to be investigated.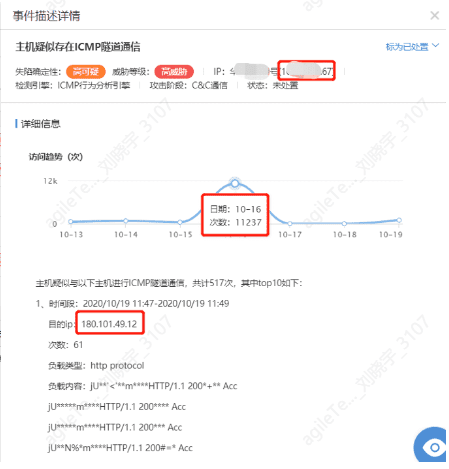
False positive exclusion methods:
1. When a sudden large number of access attempts are detected without changes in the rule library, it is considered suspicious behavior.
2. Use endpoint antivirus software to check whether there are client tools for ICMP tunneling communication on the endpoint.
Remote Task Creation in the Internal Network#
Detect whether remote service execution commands are created.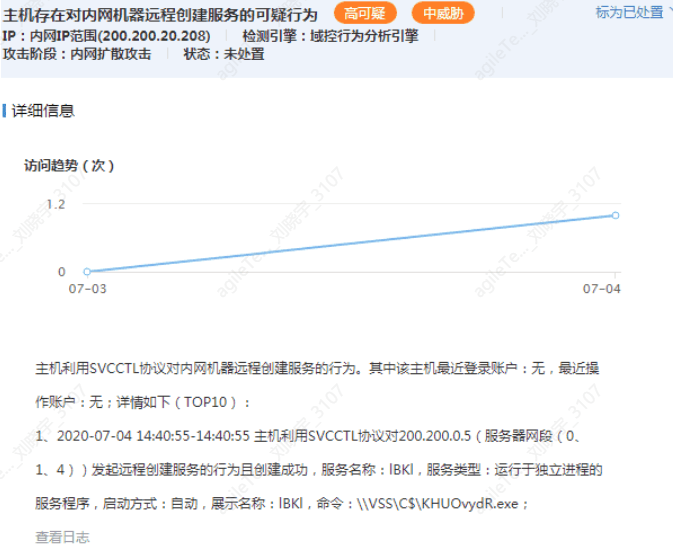
False positive exclusion methods:
1. The action of remotely creating a service will not be a false positive; the detection principle is to check whether a service is remotely created. For example, the evidence above shows that host 200.200.20.208 remotely executed a command on 200.200.0.5: \ |VSS\C$ \KHUOvydR.exe.
2. The above only indicates that a service has been created, but operational scenarios may also involve such actions, such as an administrator managing a remote host using tools like psexec (this situation has not been encountered yet). In this case, ask the client's operational personnel whether normal commands were executed. You can also roughly judge by the command executed; for example, the file name above is quite random, indicating it is likely malicious.
Remote Creation of Scheduled Tasks in the Internal Network#
Similar to remote service creation, there are rarely operational actions for creating scheduled tasks remotely.
False positive exclusion methods:
1. The evidence description above is quite clear; host 1.1.1.1 remotely created a scheduled task on host 1.1.1.2. First, 1.1.1.1 must have initiated the action to create the scheduled task, which will not be a false positive. If it shows successful creation, you can check whether there are scheduled tasks created successfully on 1.1.1.2.
2. Similar to service creation, in extreme cases, operational personnel may be doing something, but this has not been encountered yet. You can check the commands executed by the scheduled task to see what command it is scheduled to execute. Generally, if it is a scheduled PowerShell command, it is likely malicious.
Internal Network SMB One-to-Many Login#
The image shows that an attacker is using one account to attempt to log in to multiple hosts.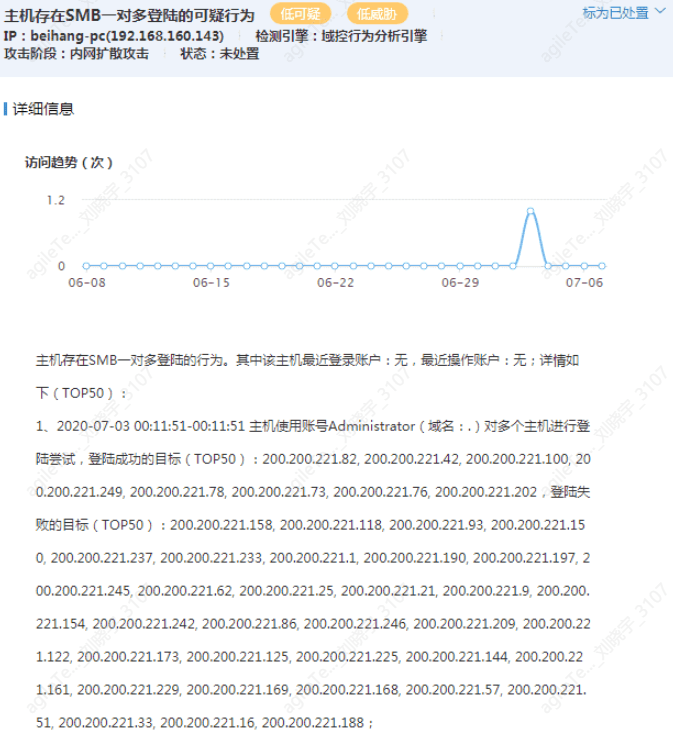
False positive exclusion methods:
1. This is generally not a false positive. When hackers obtain an account password, they will attempt to log in to multiple hosts, where the failure rate of logins is relatively high; no false positive scenarios have been found. You can check the Windows security logs for failed login logs.
Internal Network System Information Detection#
Detected that the host is performing anonymous logins to multiple hosts.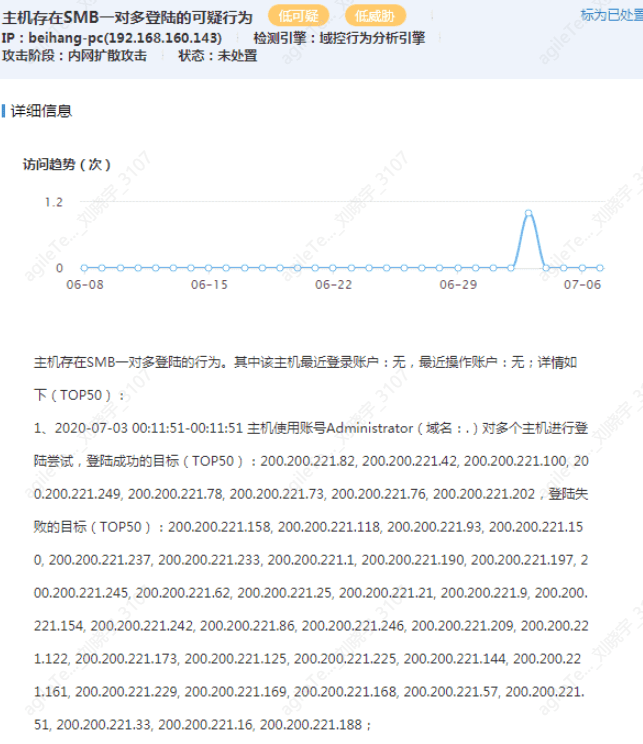
False positive exclusion methods:
This generally does not produce false positives. Driver Life often uses this method to probe the target host for system version information. The MSF smb_version module uses this method for system information detection, which manifests as anonymous logins to multiple hosts. This is a normal scenario and has not been encountered in operational scenarios.
Writing Daily Reports and Summary Reports#
Writing Daily Reports#
In normal security operation services, especially during important periods of security operation services, regardless of whether the client requests a daily report, it should be promptly written after the day's monitoring is completed. This is not only a summary of the day's work but will also provide significant help in writing the final summary report.
Daily reports should include data cycles, monitoring ranges, devices used, on-site personnel, monitoring situations of the day, emergency handling situations, etc.
Summary Report#
Compared to daily reports, summary reports are certainly not as detailed in data; they focus more on the overall defense situation throughout the project cycle. Apart from basic information such as cycles, personnel, and devices, the overall types of attacks and the distribution of various attacks need to be highlighted, as this can better expose the current weaknesses of the system. Major attack events may only be focused on the situation of that day in the daily report, but in the summary report, we can attempt to consider one or several types of attacks comprehensively, systematically sorting through some homogeneous attacks, summarizing the attacker's attack paths, and accurately locating the current issues in the system.